Introduction:
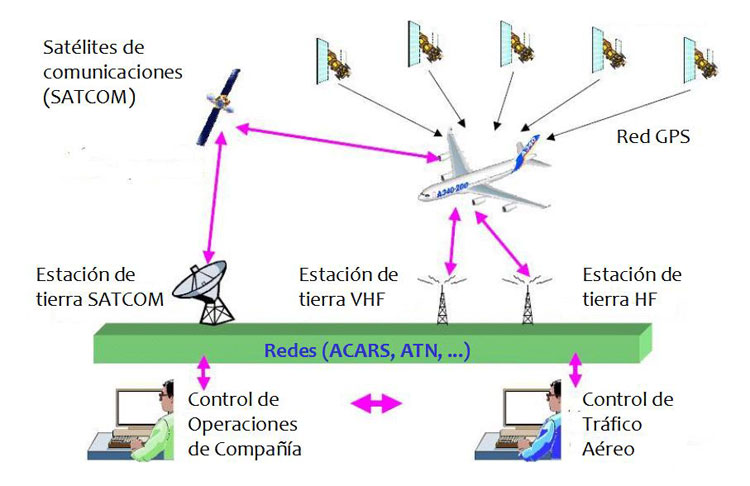
The communication capacity of aircraft in air transport has experienced a notable expansion in recent decades. At the end of the 1980s, the CNS/ATM (Communications, Navigation and Surveillance – Air Traffic Management) concept emerged, marking the beginning of the modernization of the obsolete air traffic control system. The evolution of communication systems has become as crucial as aeronautical technological advancement, playing an essential role in improving the safety and efficiency of air transportation.
Change in Communication Needs:
As air traffic grew, advanced technology allowed crews to exchange information with airlines and the air traffic management system. Since the 1980s, communications have migrated from voice to data to improve operational efficiency and security. The ability of aircraft to automatically send real-time information about their position and performance has transformed the way crews and airlines manage flights.
ACARS, INMARSAT and HFDL:
In the 1970s, the ACARS ( Aircraft Communications Addressing and Reporting System ) marked a milestone by allowing the automated sending of data through networks of ground stations connected to INMARSAT satellites. This global network has supported air communication for decades, ensuring the rapid delivery of key information. HFDL (HF data link) capability on transpolar routes also became a valuable addition.
FANS and Data Link:
The FANS Committee, established by ICAO in 1988, defined Future Air Navigation System (FANS) to provide direct data link between pilots and air traffic controllers. The implementation of FANS-A and FANS-B on models such as B747-400 and A330, A340 revolutionized air navigation and surveillance. FANS-B, launched in 2004, improved communication via HF links, Satcom and VHF data link.
The Pilot-Controller Data Link:
Although data link offers benefits such as reducing the load of voice communications, its current “slowness” prevents it from completely replacing voice communications, especially in emergency situations. The introduction of the LINK 2000+ program by Eurocontrol seeks to drive the adoption of data linking through incentives and information processing improvements.
CASCADE Program and ADS-B Surveillance:
Eurocontrol launched CASCADE in 2004, fusing communications and surveillance to improve security and reduce delays. The implementation of ADS-B ( Automatic Dependent Surveillance -Broadcast) promotes the transmission of data between aircraft for greater situational awareness. This program coordinates the integration of pan-European ground-ground communications services to optimize aeronautical information management.
USA/EUROPE Cooperation and FCS Study:
The collaboration between FAA/NASA and Eurocontrol, through the Future Communications Study (FCS), seeks to identify a globally interoperable system for ground-air communications . This study addresses operational concepts, communication requirements and alternative technologies, projecting solutions for communication needs until 2030.
Conclusion:
The constant evolution of communications in aviation, from CNS/ATM to FANS and beyond, demonstrates the importance of continuous research and development to meet the increasing demands for productivity and safety in air transportation. Initiatives like LINK 2000+ and CASCADE mark significant milestones in aviation’s digital revolution, paving the way for a more efficient and safer future in the sky

Information consulted
1.- EATMP Communications Strategy, Volume 1, Management overview. Eurocontrol , August 2003
2.- CNS/ATM Developments in Europe, a communications and surveillance perspective. JAA/FAA International Conference, Reykjavik 2003
3.- A global solution for the future ATC communications system. FAA/NASA, November 2004
4.- AIRBUS and CPDLC: FANS B progress , February 2005
5.- Move to datalink, Alex Wandels , Eurocontrol . Air Traffic Technology International 2006
6.- FANS-1/A Operations Manual version 4.0, September 2006
7.- Aeronautical Communications Panel (ACP), 10th meeting. Montreal, Canada , March 7-13, 2006
8.- ADS-B/CASCADE Workshop. Airbus industry . Palma de Mallorca, November 2007
9.- Skyway Magazine no. 46, Eurocontrol. Fall/Winter 2007 Special Issue
10.- ADS-B. IATA position, October 2007
11.- Eurocontrol /FAA Future Communications Study -Technology Assessments. Aerospace Conference , 2007
12.- Regulation No. 29/2009 of the European Commission establishing the requirements relating to data link services for the single European sky, January 16, 2009.
FOOT NOTES:
[1]SITA and ARINC are the main providers of the ACARS data link service.
[2]The main requirements that describe these systems are included in: ICAO Technical Manual, document 9705, Eurocae ED-110B/RTCA DO-280B and Eurocae ED-120/RTCA DO-290. For its part, the FANS 1/A standard is described in ARINC 622 and Eurocae ED-100/RTCA DO-258.
[3]The models that equip it are: A319, A320 and A321 and the first companies to install it in their respective fleets have been Finnair , Aeroflot and Alitalia .
[4]Elementary surveillance (ELS) provides technical and functional improvements and enhanced surveillance (EHS) provides added value at the operational level, since it improves ATC situational awareness, reduces the workload per aircraft in communications and improves flight safety.
[5]In accordance with the recently published European Commission regulation 29/2009, a deadline of February 2015 is set for all aircraft planning to fly above FL285 in the area designated as Link 2000+ to be suitably equipped. And starting in 2011, all aircraft that receive their first airworthiness certificate must be equipped to operate data link services.
[6]In Mongolia it is being installed instead of route radars, which gives an idea of its potential.

